Architecture
Categories:
Introduction
The Kubetools Recommender System (KRS) is a tool designed to assist Kubernetes administrators in optimizing their cluster configurations by recommending suitable tools based on the existing setup. This document outlines the core components of KRS and their interactions.
System Architecture
Overview
CLI (Command-Line Interface)
- The user’s primary interaction point with the system
- Provides commands for scanning, recommending tools, performing health checks, and managing system state
- Orchestrates interactions with other components
Scanner
- Responsible for interacting with the Kubernetes API to gather information about the cluster’s resources (pods, services, deployments, etc.)
- Extracts data on deployed tools and their configurations
- Stores collected data in a structured format for subsequent processing
Tool Database
- Maintains a curated database of Kubernetes tools, categorized and ranked based on various criteria (e.g., functionality, popularity, maturity)
- Serves as a knowledge base for the recommender component
Recommender
- Analyzes the scanned cluster data to identify potential tool gaps
- Leverages the tool database to suggest suitable tools based on the identified gaps and ranking criteria
- Generates recommendations in a user-friendly format
Health Checker
- Provides in-depth health checks for selected pods
- Extracts pod logs and events for analysis
- Utilizes a Language Model (LLM) to process the data and identify potential issues
- Offers recommendations for resolving identified problems
Data Storage
- Manages persistent storage of tool rankings, cluster information, and other relevant data
- Employs JSON and pickle formats for efficient data handling
Data Flow
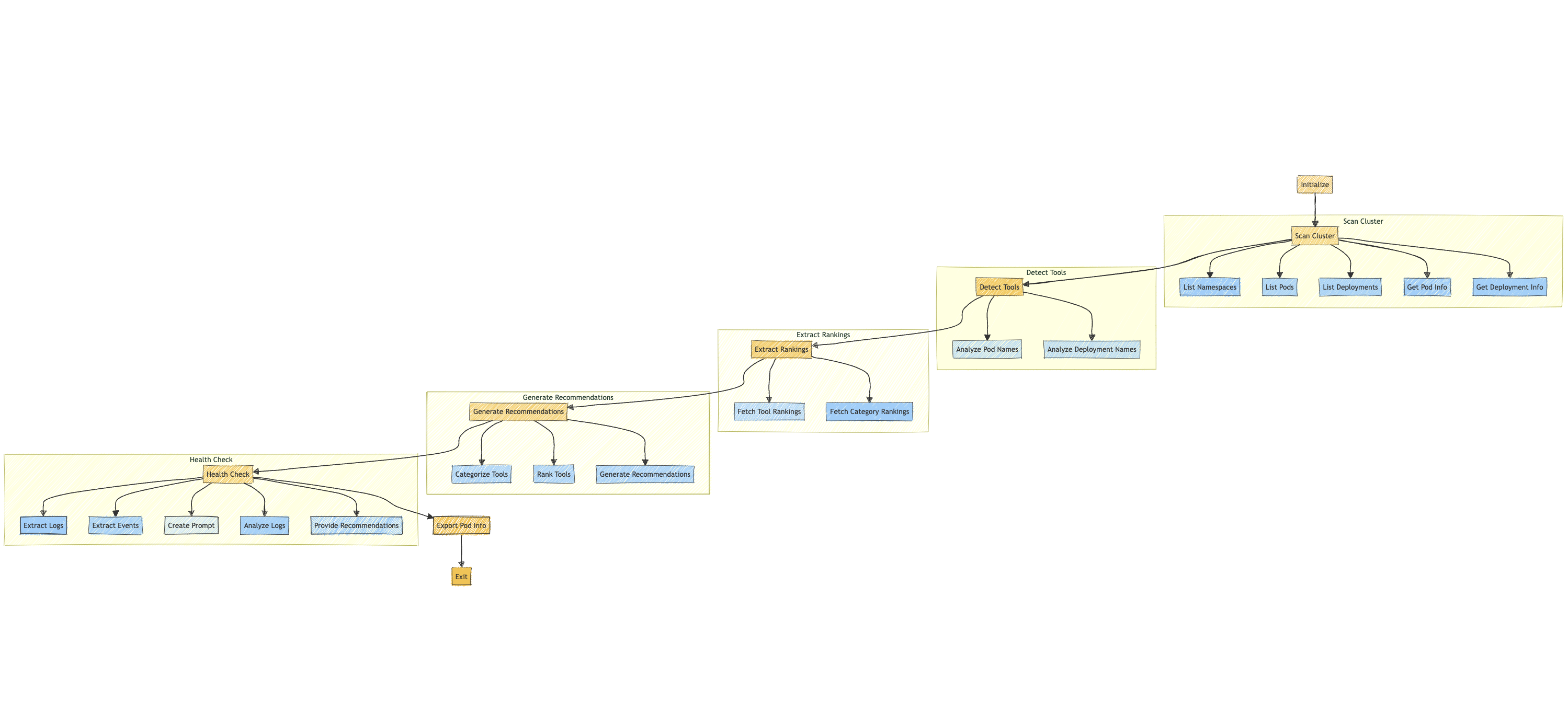
- The user initiates a scan using the CLI.
- The scanner interacts with the Kubernetes API to collect cluster data
- Collected data is stored in the data storage component
- The recommender analyzes the stored data and generates tool recommendations
- The CLI presents the recommendations to the user
- If a health check is requested, the CLI interacts with the health checker
- The health checker collects pod information, processes it using the LLM, and presents findings to the user
Deployment Architecture
KRS is designed to run as a standalone application on a machine with access to a Kubernetes cluster. It can be deployed as a containerized application or as a traditional executable.
Conclusion
KRS is a tool designed to optimize Kubernetes cluster management. It leverages a modular architecture comprising a CLI, scanner, recommender, health checker, and data storage components. By analyzing cluster data and utilizing LLM technology, KRS provides actionable insights and recommendations for tool selection and cluster health.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.